L-glutamine is a conditionally essential amino acid that plays a vital role in supporting immune function, healthy muscle growth during exercise, and managing pain from inflammation, making it beneficial for athletes, those recovering from injury, and individuals with compromised immune systems.
L-glutamine is one of the 20 basic amino acids in the human genetic code. It is a conditionally essential amino acid, meaning that dietary supplementation of L-glutamine may be required under certain conditions.
L-glutamine is the most common amino acid in human blood, with a concentration of up to 900 micromoles per liter. It plays an essential role in many biochemical processes such as a source of cellular energy.
It helps support many important homeostatic functions (which include body fluid and pH balance, and regulation of body temperature and heart rate) and the healthy functioning of a number of body tissues, particularly the immune system and the gut.
Muscle tissue accounts for about 90 percent of the l-glutamine that is synthesized in the human body, with the brain and lungs producing the majority of the remainder. The liver also synthesizes glutamine, but it receives much more glutamine from food than it produces.
The most significant dietary sources of l-glutamine are meats such as beef, chicken and fish. Additional sources include beans, beets, cabbage, parsley, spinach and wheat.
Supplementary glutamine is typically administered orally. The most common health benefit of glutamine is its role in helping support a healthy immune system.
L-Glutamine is often used to support healthy muscle growth as part of regular exercise as well as supporting healthy immune function.
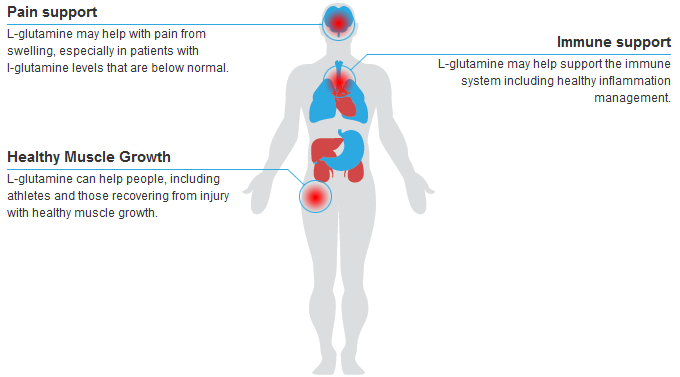
L-glutamine may help with pain from swelling, especially in patients with l-glutamine levels that are below normal.
L-glutamine can help people, including athletes and those recovering from injury with healthy muscle growth.
L-glutamine may help support the immune system including healthy inflammation management.
All amino acids support the immune system, so anyone with a compromised immune system may also need glutamine supplements. Additional areas that may indicate a need for more l-glutamine include conditions where support is required for muscle and digestive health.
You may also benefit from l-glutamine supplements if you regularly workout/exercise, especially during intense training. Glutamine levels can drop dramatically during this period, which reduces stamina, strength and recovery. It is particularly important for athletes to recover their glutamine level.
Athletes who train for endurance events (like marathons) may also reduce the amount of glutamine in their bodies. For some of these endurance athletes, it’s quite common for them to catch a minor cold after an athletic event. Some experts think that may be because of the role glutamine plays in supporting the immune system.
Shipping calculated at checkout